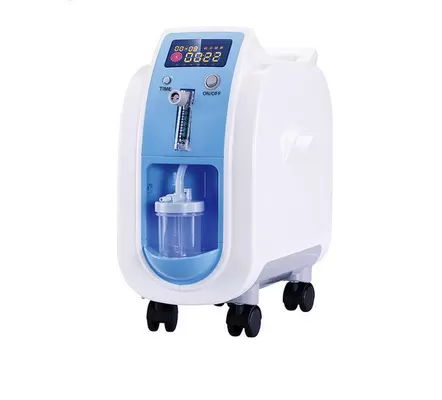
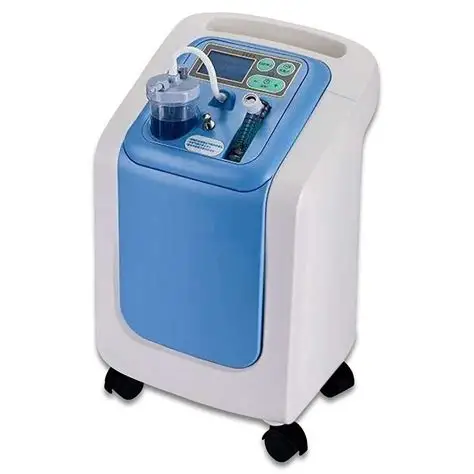
Description of an Oxygen Concentrator
1. Design and Components:
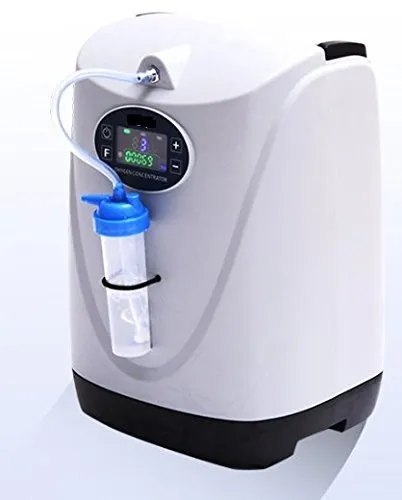
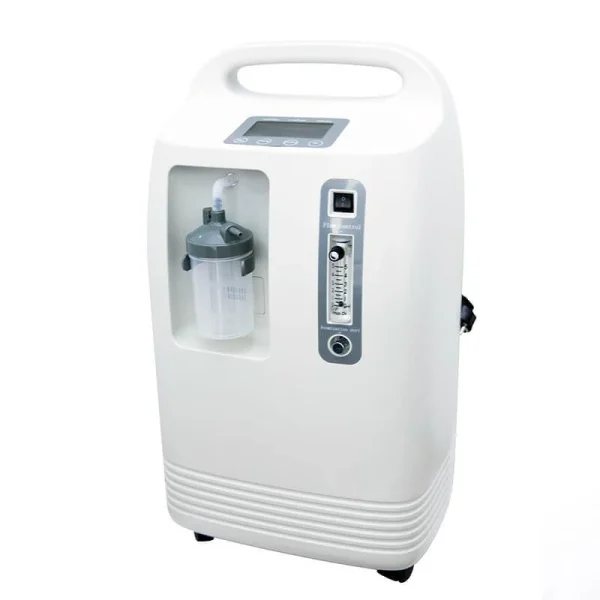
- Main Unit: The oxygen concentrator typically consists of a compact, portable unit with a control panel, power supply, and internal components that filter and concentrate oxygen.
- Oxygen Delivery System: It usually includes a nasal cannula or a face mask that delivers the concentrated oxygen directly to the patient.
- Air Filters: The device is equipped with air filters that remove impurities and provide clean air from the environment to prepare for oxygen concentration.
2. Functionality:
- Oxygen Concentration: The primary function of the device is to extract oxygen from ambient air. Ambient air is made up of approximately 21% oxygen; the concentrator can typically concentrate oxygen levels to 90% to 95%.
- Regenerative Process: The concentrator uses a process called Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA), where air is drawn into the machine, and nitrogen and other gases are separated from oxygen using molecular sieves.
- Continuous Flow or Pulse Dose: Some models offer continuous flow of oxygen, while others provide a pulse dose, releasing oxygen only when the patient inhales, thus conserving energy.
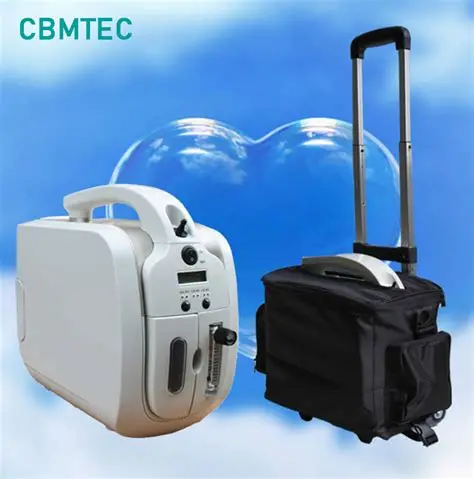
3. Portability:
- Size and Weight: Many oxygen concentrators are designed to be lightweight and portable for ease of use at home or while traveling.
- Battery Operation: Some models come equipped with battery packs that allow users to operate the device without being plugged into an electrical outlet, enhancing mobility.
4. User Interface:
- Control Panel: Features a user-friendly control panel with settings for adjusting oxygen flow, alarms for low oxygen levels, and indicators for filter maintenance.
- Alarms and Alerts: The unit typically includes alarms that alert the user to malfunctions, low oxygen levels, or when routine maintenance is needed.
5. Safety Features:
- Integrated Safety Mechanisms: Many concentrators come with built-in safety mechanisms to prevent overheating and ensure that the device operates effectively and safely.
- Automatic Shut-off: This feature helps conserve power and protect internal components if the device is not in use.
6. Applications:
- Medical Use: Primarily prescribed for patients with respiratory diseases who need supplementary oxygen to maintain adequate oxygen levels in their blood.
- Home and Hospital Use: Oxygen concentrators can be used in various settings, including homes, hospitals, and clinics, providing continuous oxygen therapy as needed.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.